Role of HR Consulting in Advancing Sustainable Development Goals in India
Chapter 1: Introduction
1.1 Introduction
Sustainable development thus is a very popular concept in recent past due to the growing concern towards environmental, social, and economic challenges of the world. It is important for organizations to incorporate sustainable practices in their organizations due to the ever- increasing globalization and integration. In this regard and within the same general framework, the United Nations (UN) launched the so-called Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in 2015, which are 17 objectives and 169 sub-targets due in 2030. This strategy goal means to enhance sustainability in developments through matters relating to poverty, inequalities, and climate change and sustainable economy goals. The current global business context is marked by the increasing appreciable influence of multinationals in many countries regarding their economic growth and sustainable development. The current Paradigm shift to sustainable development brings into focus how the multinational companies functioning from India respond to these goals. The multinationals organizations of India include Delhi, Mumbai, and Bangalore and hence are suitable areas to research more on the effects of the sustainable development goals on these multinationals’ organizations.
1.2 Research Background
The idea of sustainable development has recently emerged as a major idea in corporate business. The business world including both international and domestic firms have understood that it is high time to make the right change in favor of both the economic development and society and environment (Apostu & Gigauri, 2023). Sustainable development goals (SDGs), also called global goals since 2015, are a universal call for action towards achieving the economic, social, environmental, and political sustainability at global level by the year 2030. These goals afford organisations an opportunity to play their part in fashioning the world for the better for all people. Combination of human resource consulting and performance monitoring are significant stakeholders in the advancement of sustainable development within organizations (Aust et al., 2024). They are also charged with the duty of putting in place and or coming up with strategies and policies that are in tandem with the organizations’ goals and its value system not forgetting the health of its employees or the society in which they transact their businesses. It is the purpose of this paper to find out how the HR consulting and performance monitoring units of these multinationals can contribute in the achievement of the SDGs in the Metropolitan cities of India (Biermann et al., 2024). It will also analyse the prospects and the obstacles the above units can meet when implementing the SDGs; recommendations on their successful implementation will also be included.
1. Lack of Awareness and Commitment
Among the greatest odds faced by the HR consulting and performance monitoring units is low organizational culture of sustainable development. This situation can deny the establishment of efficient sustainable practices and policies and impede the working of such units.
Opportunity: These units can make employees and leaders become aware through raising funds or executing activities such as workshops or training and implementing awareness campaigns (Apostu & Gigauri, 2023). They can also engage the senior management in the organization to align sustainability with the aim and ethos of the organization to create the much-needed buy-in to the pursuit of the SDGs.
2. Resource Constraints
These changes will involve expenditure to effect a change and, in many cases, the HR consulting and performance monitoring units will face financial constraints in financing the changes to take place — particularly in developing countries such as India.
Opportunity: These units can follow a cost-efficient approach whereby an organization is able to focus on the major sustainability challenges as well as come up with solutions that are achievable given the resources available to the organization (Aust et al., 2024). They can also seek for more external sources of support for example through affiliation and collaborations.
3. Change Management
Environmental management can be a major problem area because it involves institutionalization, and this is very difficult to achieve. Employee and leadership resistance may have negative impact on the effective adaptation of sustainable change initiatives. Opportunity: HR consulting together with performance monitoring employees within the organization can work in conjunction with change management professionals to issues appropriate communication and engagement plans that will help foster transition to the sustainable practices (Biermann et al., 2024). It can also adequately incorporate the employees in the sustainability planning to ensure that everyone within the organization looks forward to it.
Monitoring and evaluation of accomplishments in relation to the indicators of the sdgs are critical because they help examine the efficacy of implementing sustainability programmes and adjusting work as needed (Mohiuddin et al., 2022). The HR consulting and performance monitoring units should establish a working mechanism that centralises the collection of the required data of the organisation and reporting the performance towards all the goals of the SDG to the relevant stakeholders such as employees, investors, and customers.
Finally, the case study clearly shows that HR consulting and performance monitoring units in multinationals operating in Indian metropolitan cities can indeed be a key contributor towards sustainable development and the achievement of sustainable development goals. It can be achieved through adoption of strategies and policies to promote the 17 goals and challenges can be met through partnerships and collaborations of employees’ engagement in sustainability. The achievement of sustainable development goals is a team effort, where members of many organizations have a role to portray, starting with the human resource consulting and performance monitoring groups. Indeed, the position of Human Resource (HR) has evolved from a tactical focus on clerical processes to a strategic approach in organizations.
As prime personnel officers, HR professionals are accountable for overseeing the most valuable resource of any organization, its workforce and its strategic fit. The introduction of the New SDGs has centralized the centrality of sustainability to many Human Resource activities like HR consulting and performance monitoring among others among organizations. SDG has resulted into major shift of paradigms as it relates to organization’s HR processes to ensure sustainability. Unfortunately, very little is known about how sustainable development goals might be affecting Human Resource Consulting and performance monitor in the multinationals especially in the Indian metropolitan areas. Therefore, it is pertinent to the existing studies to examine the processes, issues, and possible remedies, for SCDG7 implementation in these chosen human resource units.
1.3 Research Objective
The purpose of this study is to examine the implications of sustainable development goals for in-house Human Resource Consulting and performance monitory for multi-nationals, in the metropolitan cities of India. The specific objectives of this research can be summarized as follows:
1. To identify the methods of sustainable development goals for HR Consulting and performance monitoring units in the multinationals of Indian metropolitan
2. To analyze the importance of sustainable development goals in the multinationals of Indian metropolitan areas.
3. To evaluate the potential challenges to develop sustainable development goals for in- house HR Consulting and performance monitoring.
4. To recommend the potential process to mitigate sustainable development goals for in- house HR Consulting and performance monitoring.
1.4 Research Questions
Based on the research objectives, the following research questions are formulated:
1. What are the methods of sustainable development goals for HR Consulting and performance monitoring units in the multinationals of India?
2. How do sustainable development goals in the multinationals of Indian metropolitan areas impact in-house HR Consulting and performance monitoring?
3. What are the challenges for developing sustainable development goals for in-house HR Consulting and performance monitoring?
4. How to mitigate challenges related to sustainable development goals for in-house HR Consulting and performance monitoring?
1.5 Significance of the Study
The conclusion of this research will thus have theoretical and practical significance. From a theoretical view point, this research will complement the scant literature in sustainable development goals in HR Consulting and performance monitoring units (Niesenbaum, 2019). It will offer information on the approaches used, and obstacles encountered while achieving the objective of sustainable development in these units – with a focus on the Indian metropolitan cities. From a practical vantage there will be value add for HR professionals and decision makers in MNEs, as the study findings will offer insights regarding the effects of SD goals and such solutions as to address possible corresponding issues. It shall also wake up multinational organizations in the Indian metropolitan areas regarding the need to develop their HRM systems to incorporate sustainable development goals.
1.6 Scope and limitations
The research focuses on examining the effects of sustainable development goals on only two organizational areas: HR Consulting and performance monitoring units in MNCs operating in the metropolitan regions of India. The research does not include other HR operations and firms outside the metros of India only (Singh & Rahman, 2021). This study is therefore confined to a survey of the perceptions and experience of HR professionals and decision makers in these organizations regarding sustainable development goals in their HR processes.
1.7 Structure of the Study
The remainder of this research paper is structured as follows:
● Chapter 2: Literature Review - This chapter presents literature on General Information: Sustainable Development Goals, HR Consulting, and Performance Monitoring all focusing on Multinationals and Metropolitan Areas of India.
● Chapter 3: Research Methodology – This section outlines the design, methods, and data analysis that we used in this research.
● Chapter 4: Data Analysis and Findings - This chapter highlights the findings of the data analysis and examines the effect of SDGs on in-house HR Consulting and performance monitoring units in multinationals of Indian Metropolitan cities.
● Chapter 5: Implications of the findings, challenges, and solutions for implementing S- DGs in these HR units, and recommendations for multinationals are discussed in this chapter.
● Chapter 6: Conclusion - This chapter reemphasises the findings of this research study, the strengths and limitations of the study, and recommendations for the final and further research.
1.8 Conclusion
Sustainable development has now considered an important agenda for most organizations, and multinational business are the key agents of sustainability. Research on the subject merits given that HR units of organizations bear the responsibility of ensuring an organization’s workforce is optimally oriented towards fulfilling organizational goals, therefore, understanding how SDGs may affect these units is important. This chapter discussed the research background, aims and questions, importance, focus, and layout of this research paper. The subsequent chapters are going to uncover literature, method and result of this study mainly focusing on in-house Human Resource Consulting and performance monitor to Multinationals of Indian metropolitan areas and impact of sustainable development goals.
Chapter 2: Literature Review
2.1 Impacts of sustainable development in-house HR consulting :
According to Dziubaniuk, Ivanova-Gongne and Berdysheva, (2022), complexities and challenges influence the stakeholder networks which are focused on sustainable development goals. It has been highlighted that international stakeholder networks directly affect the sustainability goals in HR practices. Many multinational companies have focused on the local communities and well being of the projects. However, it has been highlighted that stakeholder interaction created so many challenges in country-specific projects. For a successful business establishment, it requires appropriate adaptation of the local culture. In Nepal or India, many project managers are mostly attempting to influence cultural habits effectively. But before successful sustainable HR practices, it is essential to need appropriate fieldwork.
According to Mukhuty, Upadhyay and Rothwell, (2022), sustainable development is significantly influenced through trade-off between environmental, social and economic performance. Industry 4.0 is influencing the business capacity along with cost reduction effectively. However, this strategy is effectively slow while the CSR responsibility and sustainable development play an important role. Therefore, HRM can overcome these challenges and barriers for successful business practices. So it is addressed that the digital skills gap, people-related barriers, employment threats and leadership, and organisational culture challenges have the capacity to influence susceptible development goals for long-term purposes. Project leaders should effectively maintain constant changes in specific environments and local circumstances. Also, technological adaptations influence the SCM and proper local guidance is essential for successful operations.
2.2 Performance assessment and sustainable development goals:
According to Surana, Singh and Sagar, (2020), India is becoming more developed in terms of business which influences the global business scenario. The new cities delivery mechanism is still improving and competing towards the traditional systems. There have been many positive and negative aspects in terms of SPV. Many of these developments directly come under retrofitting green field developments. Policymakers in many developing countries are increasingly seeing innovation, science and technology. Market failures and government interventions potentially fulfil the role more accurately. India's STI policy and policy priority particularly affect many societal changes. This involves specific SDGs specific goals promoting coordination between performance monitoring systems and business operations.
According to Chaturvedi, (2021), along with many countries India has collectively adopted SDGs for increasing business operations and efficiency. The government of India now prioritizes the goal of " leaving no one behind" which integrates with sustainable development goals. The country's SDG progress is highly aligned with technology and good governance. India's sustainable development goals have completely improved in the current scenario. But it has its own challenges such as the SDG India Index, the UN Sustainable Development Report, Targeted interventions and many more. To mitigate those challenges companies must have investigated operational and sociocultural aspects of the target country. In addition, many supervision and personal procession have efficiency to support proper resource adaptations.
2.2 The importance of sustainable development goals in the multinationals of Indian metropolitan areas
According to Mishra and Prateek Maheswari, (2021), in this technologically driven world, and with the emergence of the fourth industrial revolution the world intends to build up a carbon-free economy. Sustainability can enhance their productivity by reducing local manufacturing operations. Latest technologies such as AI, IoT, and others involved in mitigating the change of climate. The key holder of SDG achievements is India as it holds 1/6th of the world population. India has ambitions of housing for all elementary schools, electrifying in rural areas, and school education for all sanitation. The government has entrusted SDGs and its process. Now India widely focusing on sustainable development in energy and renewable resources and the government is investing in renewable sources. So by the advancements of the new technologies, India is developing its business module and incorporating new strategies to compete with the global market. India has become 2nd in the position of the promising market so it has seen the growth of the Indian market and development. The government has also taken initiatives to invest in 4th IR technology as they have taken the purpose for the competition in the Indian market. These new technological inventions also help to aspire to the UN SDG faster. In a greater way, these technological solutions will not be easier for India but it would be a great opportunity to make the nation more skilled and technologically updated and it would also help the country to be economically stable. However, more upskilling and reskilling methods will make the country more successful.
According to Nylund, Brem, and Nivedita Agarwal, 2021, the role of Multinational enterprises in the application of SDGs is very crucial as it initiates an innovation ecosystem and is correlated with responsible research and innovation (RRI). The concept of RRI came into this reality in 2013 by Von Schomberg and he first applied it in industry. It involves research and innovation activities where sustainability, ethical issues, and innovations are attributed. This theory has aimed to develop sustainable innovations in many organizations, companies, or other stakeholders. The radical steps of this innovation are to focus on ecosystems that are aligned with multiple levels of relationships with various stakeholders. Various kinds of partnerships are also important such as business with business, government with company or other business and other partnerships. In Multinational enterprises, RRI is embedded in innovations and it is very crucial for the business as it focuses on different fields. Therefore sustainable perspective can add a more comprehensive role in SDG achievements. It has a mixed impact on socioeconomic areas and it also provides important mobility in the ecosystem. The specific roles of RRI in MNEs create value for the business system. To make innovative changes in the environment or the ecosystems it is very important to adopt new technologies and strategies or methods. RRI is particularly important in SDG development. The relationship between RRI and the innovative ecosystem is based on the same SDG goals. With the evolving participation of the company's values, it would be more sustainable.
According to Goyal, Agarwal, and Segri (2021), the BoP segment of India has been transformed in terms of the overall number of people in extreme poverty and their low- income levels, by the year 2017. They've addressed the issue of sustainable development goals (SDGs) and their institutional voids in the environment of India. Goal no 9 of SDG, talks about Industry, innovation, and infrastructure; which indicates building resilient infrastructure, promoting inclusive and sustainable industrialization, and fostering innovation. According to the study, India, despite being a metropolitan area, lacks basic credentials like the availability of drinking water, proper sanitization, and proper waste management procedures. Their research has contributed to the literature on voids of institutions, SDG, and the Scaling of Social Enterprise. They had successfully developed three solutions to solve the problem regarding SDG implementation in India, these are- Use of technology is going to be too extensive to decrease cost and increase reach; partnership is also extremely extended across the board; and they've even focused on social innovations and business models which are affordable. According to them, entrepreneurial opportunities are primarily based on institutional voids. Therefore, social entrepreneurs address SDG at the Indian base of the pyramid which holds a low-income population having limited accessibility to resources, with a message to create societal value. Every country faces multiple environmental and socioeconomic issues, and there is underlying issues of SDGs. And India also needs various resources for sustainable development. By defending such hurdles India can improve the standard of living and can make the country more economically powerful.
2.3 The potential challenges to develop sustainable development goals for in-house HR Consulting and performance monitoring:
According to Dziubaniuk, Ivanova-Gongne and Berdysheva, (2022), Western business organizations and Governments continue to initiate and support sustainability-related projects to support regional development and directly achieve various Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The Sustainable Development Goals, established by the United Nations in 2015, set the world's sustainable development goals to be achieved by 2030. This study uses qualitative methods to analyze interview data from senior executives of an international consulting firm on sanitation programs and water supply in Nepal. This study shows that international partnerships are closely linked to the SDGs. Furthermore, the pursuit of specific goals extends to other SDGs. Achieving the Sustainable Development Goals often requires the development of networks of international stakeholders and strong partnerships or alliances at the international level. The objective of this project is to maintain a sustainable domestic water supply and ensure access to water for poor households. Access to safe drinking water improves the health and hygiene of residents and contributes to the social stability of communities. Increasing emphasis on achieving the Sustainable Development Goals through the United Nations recognizes the importance of cooperation between the 17 Sustainable Development Goals. International projects, especially in the field of environmental sustainability, often involve multiple project sponsors (e.g., government representatives, financial institutions, consultants, suppliers, local communities, and private consultants). This is a critical security issue for developing countries. The study also considers secondary data related to this and the focal company’s previously implemented projects in Nepal.
According to Mukhuty, Upadhyay, and Rothwell, (2022), Sustainability is a collaborative effort between industry, society, and the environment. Industry 4.0 benefits companies because it increases productivity, saves time, and reduces costs. But the challenges of Industry 4.0 are enormous. The numerous opportunities and benefits encourage the government to invest in the long-term development of Industry 4.0 robots in the workplace. Governments contributing to the fund include the United States; China, South Korea, Japan, Singapore, Great Britain including Germany and the European Union. Sustainable development is one of the priorities set by the SDGs and the European Commission. Human resource management (HRM) can overcome barriers using a socially responsible orientation. The challenges faced by Industry 4.0 stakeholders are identified through a comprehensive literature review. The findings revealed many people-related barriers, including resistance to change, the loss of digital skills, the growing threat of social and economic inequality in the workplace, a lack of industry-wide collaboration, and challenges in leadership and organizational culture. Human resource management can be a key factor in the development of Industry 4.0 through the use of human resource management techniques. These include strategic multi-stakeholder collaboration, holistic talent management, transformational leadership including knowledge sharing, sponsored academic research and co-developed courses, advanced technology for skills development and retention, and industrial decentralization 4.0 Concepts.
According to Ryan et al., (2020), The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are universally agreed goals set by 193 member states that outline desirable and important requirements for society. This article explains the technology can be used to achieve sustainable development goals. The HRM (Human Resources Management) case study focuses on a company operating in the service-to-service sector, which designed and developed IoT technology to help employees track and monitor their performance. They are sold as a product or service and provide companies with valuable information to improve their performance. The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) as a benchmark for measuring the success of new technologies are a good idea. By the year 2030, the 193 UN Member States will achieve what is acceptable and desirable. They are considered productive. For example, about achieving the SDGs. This article is social in nature and expands on the role of technological innovation in environmental and social sustainability. This paper highlights current practices and initiates a framework for applying practical ethics in using AI and big data to help organizations achieve the Sustainable Development Goals. The SDGs are the goals of the United Nations Declaration on Human Rights. The SDGs are based on identified human needs such as hunger, poverty and exclusion. The SDGs are described as broad and narrow goals but are broken down into more manageable and actionable goals. They are supported by targeted and measurable goals, partnerships, networks and a growing body of literature. New guidelines from the European Commission's AI expert group show how the benefits of AI can contribute to the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals. This group believes that artificial intelligence is not an end in itself, but a valuable tool to support human development, thereby contributing to the growth and well-being of people and communities, and supporting global productivity and wealth. United Nations Convention on the Rights of Cohesion and Social Development.
2.4 The potential process to mitigate sustainable development goals for in-house HR Consulting and performance monitoring
According to Kumar, Dutta and Phanden, (2024), Small and medium-sized enterprises around the world are increasing their flexibility to take advantage of changing market opportunities. Industry 4.0 technologies are designed to improve operational efficiency and have great potential for the sustainable development of small and medium enterprises. These technologies can create a more sustainable business environment by optimizing resources, recycling materials, enabling remote working, and reducing waste. The Technology, Organization, and Environment (TOE) framework provides a comprehensive review of the literature and identifies key challenges. Identified barriers were categorized into acceptance problems, lack of technical knowledge, preparation problems, and technical errors. Proper planning, process development, and process management are some of the barriers that prevent small and medium enterprises from embracing digitalization. The results also show that actual performance directly affects Small and medium-sized enterprises' readiness. This means that issues such as employee turnover, cost overruns, deadline changes, late payments and irregular processes can affect performance, leading to poor feedback, business planning and poor performance. Using the Internet of Things (IIoT) to monitor systems and prevent cyberattacks and improve supply chain process efficiency. Based on the findings of this study, managers of small and large organizations can develop effective strategies to achieve long-term goals. The research hypothesis was developed. 205 small and medium-sized manufacturing firms were surveyed. In this research, hypotheses were analyzed using partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM) to determine conceptual relationships. Risks identified included workplace hazards rather than unfamiliarity with technology at home, job stress, and limited work schedules.
According to Correia, Shahzad, Martins, and Baheer, 2024 economic development along with environmental degradation, became a threat to organizations to adopt a green innovative culture. The study proclaimed healthcare system needs to adopt sustainable practices to reduce operational costs, mitigate environmental impact, and ensure the prolonged feasibility of the services. Therefore, the emergence of GHRM practices (Green Human Resources Management) is crucial for healthcare organizations to encourage employer’s attitudes. GHRM synthesizes environmental sustainability into HR practice to promote eco-friendly policies, engage employees, and thereby manage a sustainable workforce. GHRM practices include recruitment of environment-conscious staff, awareness programs, practices regarding sustainable procurement, etc. This kind of practice can reduce energy consumption by managing wastage and thereby saving the cost. The research shows how effectively they deal with the environment to ensure sustainability, human prosperity, and industrial development. Top management systems in various organizations are basically looking for ways to implement GHRM practices to facilitate sustainability. The study also portrays how many healthcare organizations are looking for an adequate way to experiment to progress their organization to achieve sustainable performance. It also claimed that even before the growth of a sustainable economy, the environment might be degraded due to exploitation of the human. It also shows how green technology serves as a prior component to preserve the environment and improve economic growth to ensure sustainability in healthcare organizations. Therefore the enthusiasm of the top management system, to adopt a green innovation culture has been introduced by GHRM practices, according to the authors of the present paper. Not only that, the researcher even portrays light on the issue of economic development and environmental protection by examining GHRM practices along with sustainability in various organizations. Although the implementation of specific sustainable infrastructure, changing behavior of the workers, and limited resources are creating barriers to improving GHRM practices in healthcare organizations. Green technology has impacted the environment and also the economic growth of the world. The relationship between the external environment and the companies or organization isframed on Resource dependency theory. It depicts that organizations are majorly dependent upon various environmental sources.
2.5 Theoretical Framework
The Review of the past literature is conducted in this chapter and in certain instances is tested by the use of certain specific theories. In relation to the present research, the theories which have been used to test the past pieces of literature include Responsible Research and Innovation Theory and Green HRM Theory. Responsible Research and Innovation Theory
Owen et al. (2021) in their research found that the Responsible Research and Innovation Theory defines a transparent and interactive process using which innovators and societal key actors respond mutually to each other while focusing on ethical acceptability, social desirability and sustainability during the process of innovation and the resultant marketable products which ensure effective integration of technological and scientific advances into the society. The RRI was proposed to provide a blueprint for ensuring compliance with moral values during innovative research ensuring sustainability. The RRI Theory in the present research helps to explain and evaluate the importance of SDGs in multinational organisations which have embedded the concept of RRI in their business strategies and activities.
Green Human Resource Management Theory
Jiang et al. (2024) in their research state that GHRM strategies could influence the opportunities, competencies, and incentives, accessible to the employees and the social performance of the firms. The GHRM strategies have been created and tested to ensure a boost in green motivation and green performance management. The GHRM is used in the present research to explain and evaluate the different sustainability strategies and challenges of sustainability as explored in the past research papers.
2.6 Conceptual Framework
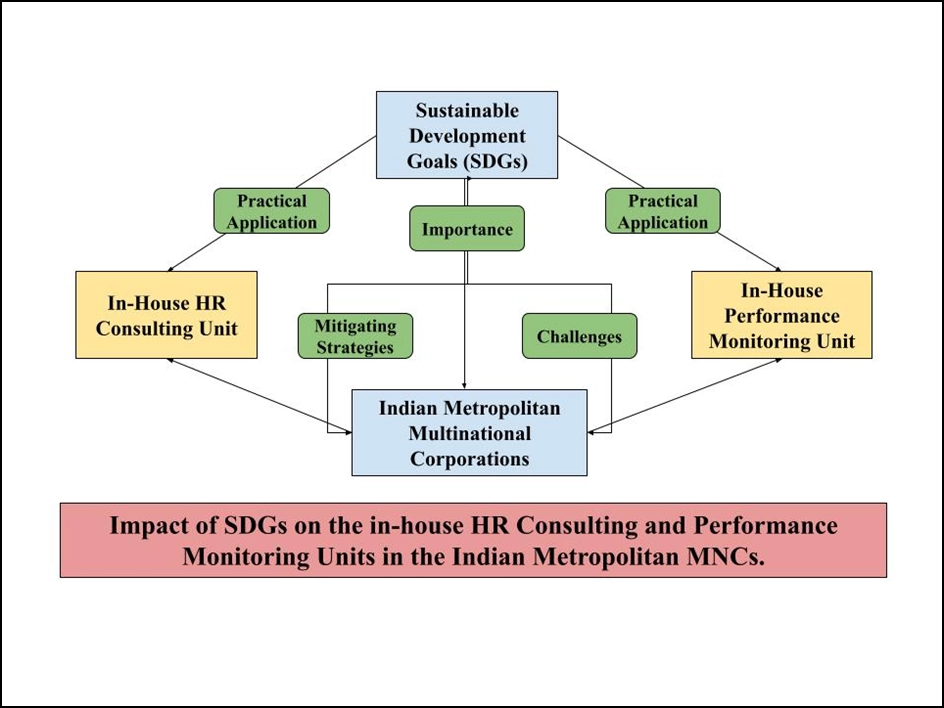
Figure 1: Conceptual Framework
(Source: Created by self)
2.7 Literature Gap
During the search of previous papers in relation to the present research topic, it was found there has been no research concentrating on the Indian Metropolitan MNCs in regards to the synergy between SDG compliance and HR functions like Counselling and performance monitoring. In this regard, the present research aims to address this gap in the research body. Moreover, it was also found that there has been little research into the integration of SDGs in specific HR functions like the HR-Counselling and Performance Measurement. This is also an aspect that requires addressing in the present research as the investigation into HR as a whole often reduces the research focus on specific functions significantly.
Chapter 3: Methodology

Figure: Research onions
Source : (Research Gate, 2019)
3.0 Introduction:
This chapter is based on different theories and tools that are completely employed by the researcher. To establish appropriate findings the researcher will choose a specific method strategy for a particular topic. This methodology chapter provides the basic concept of Idea theory and approach which help researchers find appropriate results. This chapter includes the research philosophy, approach, design, sampling method and sampling strategy, and data collection procedure analysis. Eventually, it provides a time frame and ethical considerations that are applied in this context effectively.
3.1 Research Philosophy
Research philosophy is one of the crucial aspects of research it allows the researcher to develop a base for the research. Two philosophies generally used by the researcher while conducting a study are positivism philosophy and interpretivism philosophy. Positivism philosophy gathers information through scientific method and experience while interpretivism research focuses on socially constructive ideas, subjective and multiple aspects (Alharahsheh and Pius, 2020). It allows the researcher to collect data by using observation and interviews. Therefore this research is based on qualitative methodology so the research used interpretivism philosophy for evaluating the study. It will provide the most conscious viewpoints regarding the sustainable development goals and in-house HR consulting, also provide a details overview of performance monitoring.
3.2 Research Approach
The research approach is a procedure which analyses collects and interprets specific data. Two types of research approaches are generally used by the researcher these include the inductive approach and the deductive approach. The detective approach develops a comprehensive research strategy which helps the researcher to conclude by using different hypotheses on existing theories. Alternatively, the inductive approach is a bottom-up process which helps such a to develop a theory based on previous research. In this research, the researcher has adopted an inductive research approach to analysing the study (Proudfoot, 2023). It is useful for understanding innovative and critical phenomena and provides new or appropriate insight into the topic. It provides a better inside view of performance monitoring data in different multinationals of Indian metropolitan and provides and compact full idea for further evaluation. The inductive approach provides flexibility and a generic new theory which helps to identify patterns by utilising different perspectives.
3.3 Research Design
Research design is a crucial factor for evaluating methodology. Three distinct types of Research design are generally used in the research these include exploratory, explanatory and descriptive Research design. The research design set a tone or objective of the study. If the objectives and Research question are not fully prepared the researcher mostly utilises explanatory and exploratory design methods (Turale, 2020). In this context, the researcher chooses a descriptive design method for the study. While the Research questions are objectives are concise and provide a brief idea about the findings the researcher specifically used a descriptive Research design. In this context, the researcher has used descriptive research designs. This Research design provides a comprehensive understanding of the topic by capturing many aspects. Also, it is cost-effective, easy to contact and can collect multiple types of data. This topic identifies different patterns and trends related to the human resource performance of Indian metropolitan and compares them with sustainable development goals.
3.4 Sampling Method and Sample Size
A sampling method is a process for selecting individuals or groups to participate in research and draw a valid conclusion. It allows researchers to adopt specific statistical data and provide the most relevant information. Generally, there are two kinds of sampling methods commonly used by the researcher such as probability sampling method and non-probability sampling method. The probability sample method is reduced by generalising reliable data and increasing the validity of the research (Andrade, 2020). However non-probability sampling method is a cost-effective and quick approach for collecting data. It provides a detailed description of the sample which can help the researcher to find the appropriate conclusion. The study is based on secondary qualitative so the probability sampling method has been used for the research. It is easy to implement and improve precision in this context. The sample size is important and maintains the reliability and validity of the study. A large sample size provides more appropriate and accurate results while a small sample size can easy to analyse but provides a certain limit of error (Rahman, 2023). An accurate sample size has statistical significance and effectively narrows the margin of error. It reduces the bias of the research and more precisely generalizes the findings. In this study, 20 articles will be selected from a valid and reliable source by following proper intrusion and exclusion criteria.
3.5 Research Strategy
Research strategy mostly guides the researcher through the process of conducting a specific study. It is a step-by-step guideline that helps researchers stay focused produce quality results and save time. There are several strategies have been used to incorporate the methodology. These are experimental strategy, case study strategy, interviews and surveys. These strategies enable the researcher to extract specific data from relevant sources. This study is based on secondary qualitative methodology showing the researcher used a secondary literature review-based research strategy. It provides more detail and comprehensive ideas about the topic and highlights different aspects which need to be evaluated or further results. It is also useful for building knowledge and providing ideas about its future scope by identifying research gaps. In this context, this study provides ideas about sustainable development goals and their relation with each other consulting and performance. Also, evaluate different monitoring units specifically in multinationals of Indian metropolitan.
3.6 Data Collection Methods
The data-gathering method is a technique which helps the researcher to collect information and draw a conclusion which is directly aligned with the study (Chigbu et al., 2023). It allows researchers to prepare the overall framework of the research and draw conclusions by saving time. In this research, the data for the research is collected by using a secondary literature review-based study. The researcher has been collecting data from various reliable sources such as Elsevier, Google Scholar, Wiley, Science Direct and JSTOR. The articles are collected by using several exclusion and inclusion criteria or some Boolean operators such as OR and AND. The most recently published article with English and PDF structure after 2020 has been selected. Articles that are not reliable published before 2020 and not in PDF format have been rejected due to maintaining the reliability and the validity of the research.
3.7 Data analysis methods :
The data analysis is important for the researcher it helps the researcher to draw an appropriate consolation regarding the study and provide recommendations based on extracted data. Several types of data analysis have been utilized to maintain The authenticity of the research. This research is based on secondary qualitative methodology and evaluated data by using different literature reviews (Mwita, 2022). In this study, the researcher has used thematic analysis to evaluate the data. It provides the most useful information about sustainable development goals for in-house human resource performance and consulting monitoring units in the multinational Indian metropolitan. It also uncovers the inside of the topic and helps to explore subjective information.
3.8 Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations are a more important contact of the researcher especially in the case of secondary data evaluation features obtained from the literature review. As the data in this study is based on secondary qualitative data the researcher has to maintain proper validity, authenticity and anonymity of the research. It is essential to obtain consent during data collection and acknowledge the data source appropriately (Husband, 2020). Therefore the ethical consideration in the study is that the researcher takes proper consent to maintain confidentiality while conducting the research. The data used to evaluate the research is mostly reliable and accurate and transparency is maintained properly. Also, previous authors have been acknowledged and the researcher ensures the reliability, authenticity and validity of the research. Personal data is not disclosed without concern and the procedure follows ethical guidelines rich enhance the reliability and validity of the study.
3.9 Time Frame
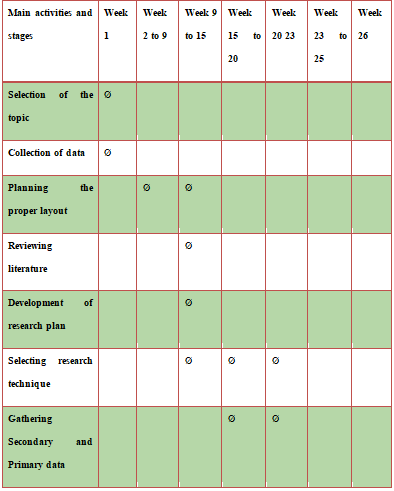
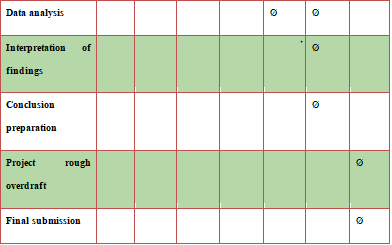
3.10 Summary
Finally, this chapter discusses the research methodology and provides all the important parameters which are needed to be implemented to validate the research. In this study, it may be concluded that the interpretivism philosophy, an inductive approach has been used which provides a comprehensive and concise idea about the topic. The secondary literature review base strategy is used and different literature is selected from reliable sources. The probability sampling technique has been adopted and thematic analysis is conducted for further evaluation. This provides more detailed knowledge regarding the topic. Finally, a time frame has been provided and ethical considerations should be discussed which ensure the authenticity of the research.
Chapter 4: Data findings and analysis
4.1 Chapter Overview
The following chapter on data findings and analysis is critical for evaluating extracted data out of reliable secondary resources to answer the research questions set earlier in the research introduction chapter. Drawing back evidence from the secondary sources, the data will be used in this chapter to draw conclusions and support hypotheses. Showing the readers what the data tells about the research theme, this chapter will discuss the impact of sustainable development goals for in-house HR consulting and performance monitoring units in the context of Indian metropolitan multinationals.
4.2 Secondary qualitative findings
Refer to Appendix 1
4.3 Thematic analysis based on identified themes in the study
Theme 1: HRM and sustainability reporting practices in Indian MNCs
Bhowmik and Dutta (2022) reports that India is nearly 25% of global groundwater extractor, which makes India highly responsible to take on sustainable action on conservation and restoration of groundwater as part of the UN’s charter of sustainable development. Sarangi and Jabbal (2024) presents data that as India consists of both developed and underdeveloped urban and rural areas, therefore, consideration of resource consumption, environmental degradation and social inequality would present a severe challenge in sustainability reporting practices for Indian MNC to plan on countering these issues to achieve respective sustainable development goals.
Theme 2: ESG-based HR performance and in-house training at metropolitan Indian industries
Singhania and Saini (2022) mention Reliance Industries Limited (RIL) could be an ideal example of an Indian conglomerate that has taken responsible action over the years to appeal to socially-conscious investors and create value in their portfolios. Noronha et al. (2022) refers that ESG practices and in-house training to create socially-responsible businesses align with the rise of global production networks (GPNs) that also support metropolitan Indian industries to increase their profits through economic upgrading and social upgrading.
Theme 3: Meeting SDG goals at Indian footprints
According to Biswas and Tiwari (2021), the CSR spent by the Indian companies has come down by 6% – 7% which is a positive development toward SDGs. Mishra and Maheshwari (2020) discovers that the fourth industrial revolution has made it possible for Indian companies to build a more inclusive and sustainable society through technology in a country like India for utilising SDG goals.
Theme 4: STI based policy in India influencing SDGs implementation
Surana, Singh and Sagar (2020) mentions that strengthening STI-based policy can emphasise economic development and employment generation which can positively influence Indian society. Aktar, Harun and Alam (2020) say that STI offers leveraging affordable and clean energy which is considered as the base of sustainable development throughout.
Theme 5: Indian businesses strategy in achieving SDGs
Chaturvedi (2021) claims the vision of the Indian Government for ‘New India’ to give priority to high-end manufacturing, infrastructure, effective healthcare policies, information technology, all aligned to SDGs. Sharma and Varshney (2023) continue with the discussion to acknowledge India's role as possibly the biggest to foster and empower self-reliance for developing societies like India to experience the benefits of SDGs to the fullest.
Theme 6: “Leaving no one behind” agenda and SDGs
According to Sénit (2020), participation within UNHQ-based negotiations can open further possibilities for civil societies in India and other developing countries to penetrate SDG initiatives more into deep roots toward impromptu developments across all levels in society. Khalid, Sharma and Dubey (2021) identify that the primary concern to SDG accomplishment in India still could be addressing large-scale socioeconomic inequality to some extent despite the recent efforts by the Indian government and Indian business communities which has in fact shown positive outcomes to uplift millions in India out of poverty in recent years.
Theme 7: Partnering SDGs and HR practices at Indian metropolitan industry
Dwivedi and Bhattacharjee (2024) find that the post-pandemic world has changed in such a way that there has come out a huge opportunity for a human-centric approach to HRM. Khalique et al. (2021) even claims one of such positive human-centric approaches could be in offering decent work environments via including equal opportunities and equal pay for overall economic development in MNCs across India. This initiative can eventually supplement through achieving strategic goals as per the SDG requirements.
Theme 8: Industrial clusters and SDG policies in Indian metropolitans
The literature evidence of Bharat, Dkhar and Abraham (2020) highlighted that Sustainable Development Goal 6 has a positive impact on the development of human resources and their performance monitoring in the Indian Sanitation Chain. For instance, scarcity of human resources has affected the wide-scale adoption of Sanitation policies in the Indian Metropolitan and rural segments. CSOs, Non-government organisations play an instrumental role in providing management and consulting training to the labour force in India for the smooth execution of the Indian Sanitation policy based on the requirements of SDG 6. In a similar context, Chakraborty (2024) opined that SDG-based performance monitoring units have a positive influence on human capital development in different industrial clusters. This has helped India to reach a GDP of $3.75 Trillion. The researchers extensively focus on the impact of SDG on in-house HR consulting units deployment across different industrial clusters; this has helped to counter the challenges of spatial inequalities in Gujarat.
Theme 9: Challenges of managing SDG projects within HR practices in MNCs
As per the opinion of Mukhuty, Upadhyay, and Rothwell, (2022), the sustainable development of MNCs is heavily dependent on the interrelationship between the environmental, social and economic needs of the businesses. The scarcity of skilled human resources and lack of poor performance and management efforts might harm the final deliverables of SDG projects. For instance, socio-economic inequalities, change resistance and skill deficiency might influence people-related barriers in SDG projects. On a different note, Dziubaniuk, Ivanova-Gongne and Berdysheva, (2022) argued that inconsistent interaction between International stakeholders had a negative outcome on the adoption of SDG projects in India. For instance, ineffective governance mechanisms in multi-stakeholder SDG projects might increase the environmental impact of SDG projects in Indian Metropolitan cities.
Theme 10: Improving the implementation outcome of SDG projects in India with Strategic HR consulting and performance monitoring practices.
As per the evidence of Mahajan et al., (2022), the Indian Government partnered with Navratna companies to enforce a strong public-private partnership while executing SDG projects. Hence, SDG 9 requirements of sustainable industrialisation, resilient infrastructure development can be fulfilled through HR consulting. Additionally, the functioning of Narvratna companies helps in the deployment of in-house HR performance unit to fulfill the manpower requirements of SDG projects in India. In a similar context, Ebikozien et al., (2024) mentioned that the skill development requirements in the SDG projects in India can be fulfilled by achieving the standards of SDG 8.
4.4 Comparisons of thematic findings with research objectives & literature
Sustainable development goals for HR Consulting and performance monitoring units of Indian metropolitans MNCs
From theme 8, it can be noticed that SDG 6 significantly impacts the performance and growth of human resources in Indian metropolitan MNCs. NGOs play an essential role in terms of giving effective consulting and governance training to the workers of metropolitan MNCs for the implementation of Sanitisation policies by focusing on SDG 6. The management of SDG 6 in human resources helps in developing the consulting performance units in India to maintain sustainability in the business operations of metropolitan MNCs (Rahigude et al., 2022). SDG 6 enables MNCs to incorporate human-centric strategies within their working culture which helps them in developing their performance by evolving their human resources. Hence, it can be interpreted that SDG 6 is most suitable for expanding human resource performance monitoring departments and consulting in the metropolitan MNCs of India.
Significance of SDGs in HRM for Indian MNCs of metropolitan areas
From the findings of theme 5, it can be defined that SDGs in the metropolitan areas of Indian MNCs helped in designing healthcare policies, manufacturing infrastructure, and information technology which enabled them to develop their performance in the market. Moreover, theme 7 indicated that SDGs enable metropolitan MNCs to adopt human-centric approaches in their business operations to enhance their performance in the market. SDGs help in improving the manpower in metropolitan MNCs by increasing jobs in rural areas which contributes to their enhanced performance in the Indian market (Khemka et al., 2022). Therefore, it can be stated that SDGs play a significant role in developing the HRM practices of Indian metropolitan MNCs by increasing gender equality in the workforce. SDG Issues faced by in-housed HR consultants in performance units of Indian metropolitan based MNCs
Based on the findings of theme 9, the sustainability development goal-based problems faced by the HR consultants in Indian metropolitan-based MNCs such as Wipro and Infosys are problems in retaining skilled employees due to lack of adequate finances. Moreover, the failure of the Indian metropolitan companies to provide adequate amounts of compensation to the employees acts as a challenge to the retention of skilled employees (Priyanka, et al., 2023). This condition compels Indian metropolitan organisations to suffer from challenges related to diversity and inclusion. In this prospect, the HR professionals of a leading Indian MNC company, Wipro faced SDG-based challenges related to gender discrimination and inequalities of the socio-economic conditions of its workers.
Recommended strategies for SDG implementation in HR consulting practices for sustainable performance units of metropolitan MNC in India
Depending on the findings of theme 10, it can be highlighted that the deployment of performance units for HR professionals within the company will help the HR consultants to mitigate the problems related to the scarcity of skilled employees in metropolitan MNCs of India. In this prospect, the leading metropolitan MNC of India, Wipro has already launched a Group of Employee Resources (ERG) for creating a community-based culture among its employees in the workplace. Wipro has also developed a program named WOW, with the sole aim of ensuring the provision of a positive workplace environment to its female employees through their representation in leadership positions(Diversity and Inclusion- Wipro careers, 2024).
4.5 Limitations of thematic analysis & findings
The above thematic findings majorly focus on HRM and HR consulting practices to meet the environmental, social and governance requirements of SDG projects in Indian Metropolitan cities. However, Pathak and Deshkar, (2023), mentioned that a huge amount of SDG projects in India fail in the rural regions due to persistent social inequalities. The above themes failed to introspect the sustainable reporting practices and HRM processes used in the rural regions in India. The inclusion of only 20 piecessecondary literature might not be able to generalise the overall findings for the focus study groups, “Indian Metropolitan Cities”.
4.6 Discussion linking research question
4.6.1 RQ1: The methods of sustainable development goals for HR Consulting and performance
The Sustainable Development Goals of SDGs were established by emphasizing the integration of sustainability practices effectively. The organization and operations for the multifunction facilities provide an idea about each area of consulting and their performance monitoring system effectively. The methodological adoption highlights the important alignment aspects regarding the operation of efficiency with SDGs in an effective way.
Linking with objectives:
Integration of SDGs into Talent Management
HR initiative and consulting Services insurance about the SDG principles which are immediate into the talent acquisition process where the development of strategies highlights the diversity and inclusion criteria as a gender equality. As a multinational implementation process, the gender priority service initiative and inclusive hiring practices can flip the important marginalization groups in a leadership pipeline prioritized (Mujtaba and Mubarik, 2022). Quality education provides an idea about the strong employment training program that is light with the continuous learning skill and development process. Generally, it also signifies the educational institutions as their up-skill process to improve the communications which reflects the organization's commitment to the education. The schematic approach of the study provides an idea about the sustainability approaches regarding the Indian MNCs.
Developing green workplace and policies
Involvement of green workplace and policies significantly and deliberately highlight the impartial HR strategies which have a clear effect on the ESG best Eicher performance and in-house training program in the Indian industry. The theoretical study approach provides an idea about the environmental social and government ethics that are related to sustainable operations and indicates the importance of green HR policies. Naturally, it encourages remote work and paperless operation comprehensively (Faeni, 2024). Energy efficiency in the workplace can reduce the carbon footprint. Moreover, KPIs significantly highlight the employee management programme to contribute the sustainability practices to minimize the research stages or adopt eco-friendly practices.
Performance Monitoring System for Ethical and Sustainable Practices
The performance monitoring units integrated with the sustainability approaches by evaluating several frameworks such as the triple bottom line approach and SDG reporting tool. This type of tool provides proper alignment with the business leaders in promotional sustainable practices. The study also signifies the important aspects that are related to the lifestyle and SDGs review waste system. Employees and departments are evaluated based on the social environment and economic contribution whereas the store account's ability to sustain actions totally depends on the reporting tools. This type of tool indicates the involvement of the SDG reporting aspect where the performance-based dashboard monitors who created in the term of socially responsible businesses in an Indian way.
Workforce Well-being and Equity Initiatives
The involvement of external stakeholders provides an idea about the process of sustainability practice where the community development project and global partnership are the important ones. Where the comprehensive understanding of the health care benefits provides an idea about the current initiative to cover the mental health resources that are introduced in the statistical adoption process of SDGs (Creary, Rothbard and Scruggs, 2021). The living which policies mostly promote economic growth and reduce the inequalities whereas the HR strategies in yours about the CRP structures to the employees. Employees mark it as the most beneficial aspect in India.
Collaboration
The multiple stag holder signifies the important factors that are related to multinational engagement with external stakeholders. The foster sustainability practices indicate strong community engagement in the development of projects where the HR collaborations critically evaluate the process of every statement of Government and NGOs. To launch new types of initiatives such as Steel training, manipulating the unemployed youth or accessing the clear water which is directly related to industrial clusters and SDGs policies in India (Dolla and Laishram, 2020). The strong global partnership program highlights the International sustainability forums where the HR consultancy report provides an idea about the based practices and innovative approaches to HR consulting units to adopt best practices. The study highlights the strong underpinning process under the role of human resource practices.
Adopting Technological Sustainability
The performance monitoring system signifies a comprehensive understanding of where the technology integration process can be evaluated by using several tools to achieve SDG compliance effectively. However, the important analytical aspects of the technology adoption highlight AI-driven analysis and a comprehensive modelling system of digital workspaces. The driven analytical system is a high-tech process where the data analysis is mostly measured toward sustainability growth by offering the actionable in science comprehensively (Patma, et al, 2021). The digital workshop plan mostly helps in transmitting the digital operating system which reduces resource deficiency and dependency at the same time. The theoretical underpin provides an idea about the strong relation where the industrial clusters and HD policies in Indian metropolitan cities can be divided into several patterns by the sector-dal investments and employments.
4.6.2 RQ2: Sustainable development goals in the multinationals of Indian metropolitan areas impact in-house HR Consulting and performance monitoring
The sustainable development goal for the important global framework is to promote the growth aspects in the environment and conservation way. For the multinational operating system, the Indian metropolitan areas integrated the SDGs into the house of HR consulting and performance monitoring process. It is one of the most crucial aspects for an organization to manage its standards effectively. From the long-term perspective, the operations provide an idea about the exploration process of SDGs in the Eicher consulting system. The proper organization of authority of the study provides an idea about the current application if those are related to the partnership programs in the HR practices of the Indian metropolitan industry.
Linking with objectives:
Strategic alignment of HR practices with SDGs
The HR consulting units in India have multinational aspects to adopt the policies for better alignment in the workforce management with SDGs objects such as diversity and inclusion, and skill development. The HR consulting units have signifies the inclusive criteria by hiring practices forecasting gender balance in the workplace. The metropolitan areas in India such as Mumbai and Bangalore organized equal opportunities for women minorities. Mostly it helps in community engagement according to the leadership role (Bilderback, 2024). A mathematical understanding of the study provides an idea about the comprehensive modulation system of SDGs which significantly provides an idea about the upskilling process by ensuring the organizations in first changing markets
Sustainability approaches in the performance matrix
Apartments monitoring approaches provide a comprehensive idea to the Indian metropolitan multinational aspects regarding the sustainability matrices which directly suits the comprehensive understanding of social compact Ness where the CO-creating factors mostly underpin sustainable operations. However, one of the important approaches such as a triple bottom line helps to review the social environment's involvement in the economic impacts. The holistic view ensures accountability of the sustainable practices individually which the department of organizational levels highlights the strong emblem in the modular understanding of thematic analysis (Ali, Kaurand Khan, 2023). Agent of the study partially allied in the model understanding process where the best examples of deadly or Hyderabad signifies the energy efficient technology and their reduction in Waste management system of supply chain management.
Employee well-being and equity initiative
The employee retention program has a major contribution on the sustainability aspects comprehensively which ensures that the employee while being is the main aspect of the study. The proper alignment process of the study mostly remarks about the partnership-related program that can affect the employee retention program. The proper understanding of prospects also provides an insight into the industrial clusters regarding SDG policies, health safety programs and equitable compensation as important factors. Eicher unit implemented robust wellness initiatives where mental health support prevented the health care programs and organic workplace design (Ongom, 2023). Equitable compensation signifies the importance of decent work and comprehensive economic growth in metropolitan multinational organizations by prioritizing living wages and equitable pay structures. It provides basic assurance behind the Eicher consultants and improves workforce miracles.
Technology integration for sustainability monitoring
The performance monitoring system indicates the comprehensive idea which the unit-based understanding signifies an advanced technology process to ensure the seamless tracking and sustainability aspect. It has a positive inside for the betterment process of their goals where the AI and Big Data analytics and digital work process play a crucial role. Moreover, the study dynamics signifies the main concerns as a developing parameter in the country for sustainable growth which also mentions the importance of civil society and their technology adoption process. AI-based approaches signify the importance of several tools such as AI given dashboard which provides real-time insight into the progress towards SDFs which enables the manager to identify gaps and implement corrective actions (Neves, de Castro Neto and Aparicio, 2020). However, digital workspaces provide an idea about digital operation which mostly reduces paper usage and minimizes the imran mental impact in an effective why several cities such as Chennai and Pune use the virtual collaboration options as tools for sustainable approaches. The study strongly related to the importance of concerned by developing the countries and sustainable development and goals.
4.6.3 RQ3: The challenges for developing sustainable development goals for in-house HR
Consulting and performance monitoring
The study has tried to develop multiple potential challenges for creating sustainable development goals for in-house performance monitoring. This can face multiple challenges in multinational corporations which are located within the metropolitan areas. All the challenges have been based on different operational, cultural and strategic issues.
Linking with objectives:
Cultural and regional differences
Multiple companies which are operating in the Indian MNCs have faced multiple hurdles of shaping regional and cultural complexities. Indian metro cities are considered as one of the important hubs of diversity where employees come from multiple different socioeconomic backgrounds. This can have an impact on the overall work culture and change the approach towards sustainability. Multiple regions have prioritised environmental conservation and multiple cities have focused on equity and inclusion (Hong, et al., 2022). This kind of disparity can make it highly dangerous to create a unified organisation-wide SDG for HR and performance monitoring.
Capacity building and training
An organisation needs to invest in multiple attending themes for addressing issues of knowledge gap regarding SDG frameworks, ESG principles and sustainability matrix. Multiple workshops, certifications and partnerships can be created with sustainability consultants so that HR professionals can improve to integrate sustainability within performance monitoring systems.
Short-term productivity
HR consultation and performance monitoring can stress immediate results such as employee efficiency retention rates and operational success. Sustainable development goals have tried to provide long-term commitment towards the incremental process. There has to be a balance between the two timelines otherwise there can be challenges for HR teams in the MNC for operating within the fast-paced Metropolis of India.
Resistance regarding change
There can be a huge problem in integrating sustainability within the HR practices as it can often disrupt the old processes. Employees and leaders might resist adopting multiple sustainability performance indicators or ESC frameworks because of fear of increased workloads. There can be unfair outcomes and discomfort regarding unfamiliar situations.
Measurement and accountability challenges
There are multiple financial matrices and sustainability outcomes in the HR process such as employee well-being and diversity which are quite difficult to measure. This can create multiple barriers to accountable performance monitoring mechanisms which are aligned with sustainable development goals.
Collaboration within global and local teams
Within Global sustainability teams and local HR leaders, Global SDG frameworks need to be localised according to the context of Indian metropolitan cities so that initiatives which are created can be ambitious and practical. There have to be regular cross-functional meetings which can mitigate the gap between global strategy and local execution (Hailu, et al., 2020). The global and local tensions can be resolved by promoting cross-functional meetings.
Economic pressure and resource constraints
Indian metropolitan areas are popular for providing comparative MNC environments. In this scenario, there can be economic growth and cost efficiency which can try to overlook the sustainability efforts. Sustainable HR practices need to be implemented to provide investment in tools and resources that cannot be feasible for all firms.
Global and Local Tensions
The Indian MNCs often face multiple tensions within global corporate sustainability measures and the operational realities of the local area. There are multiple Global headquarters which have tried to stress on ambitious SDG initiatives (Shaw, et al., 2023). Local teams have also struggled to implement different initiatives because of resource constraints and regulatory challenges within Indian cities.
4.6.4 RQ4: MItigating challenges related to sustainable development goals for in-house HR Consulting and performance monitoring
The research has been based on mitigating the challenges regarding implementing SDG Goals in performance monitoring in units of Indian MNCs. Multiple firms can try to use different strategies for adopting consultation and performance monitoring.
Linking with objectives
Cultural Adaptation
Organisations need to localise the initiative by integrating employees from different cultural and regional backgrounds in planning and implementation. Multiple firms need to customize based on regional priorities and workforce preferences so that buy-in can be created and resistance can be minimised (Waizenegger, et al., 2020). Teacher consulting units can organise multiple regional focus groups so that sustainability priorities can be identified that can be aligned with employees in different Indian metros.
SDG and KPI's
The HR team can easily integrate sustainability Matrix within the old KPI why providing employee performance reviews. Different criteria related to environmental stewardship and DEI initiatives. This approach can balance short-term productivity with long-term sustainability goals.
Change management and Communication
HR leaders need to productively address multiple resistance to change with the help of transparent communication and implemental implementation strategies (Sarwal, et al., 2021). HR leaders can provide improved employee welding and stronger employee brandy for promoting employee engagement.
Technology for measurement
HR managers can use data-driven tools and technology so that they can simplify the process of measuring sustainability results. They can try to use advanced ether analytics platforms so that Matrix can be tracked such as employee will be and Diversity ratios. HR managers can create carbon footprint contributions to workforces.
Regulatory compliance and public-private partnerships
HR-based SDG initiatives are needed according to the sustainability regulations of India which are facing regular evolution. There have to be corporate social responsibility mandates that can create synergies (Men, Yue and Liu, 2020). Multiple brands and partnerships with government agencies NGOs and local communities so that the impact can be boosted and sustainability goals are accepted within the Indian MNCs.
Employee Incentives:
HR-based brands need to provide incentives as a practical approach so that active participation is encouraged in achieving sustainable development goals in HR consulting and performance monitoring. Focused initiatives are needed to be associated such as bonus recognition programs and clear advancement so that efforts and organisational goals are aligned. Employees and the teams are needed to demonstrate sustainable initiatives such as providing diversity and inclusion programs so that environmental impacts are mitigated in office operations (Kostruba, 2021). There have to be multiple incentives such as performance-based bonuses that can be aligned with specific SDG Matrix which can drive further commitment. All these incentives cannot just enhance employee engagement but can provide a sustainability-focused culture within the organisation. Recognise contributions towards SDG improvements and provide sustainability outcomes.
Chapter 5: Conclusion and Recommendations
5.1 Conclusion
Based on the above research one of the major findings is that sustainable development goals play a significant role in the development and establishment of the human resource management practices of the Indian Metropolitan MNCs through the improvement in the gender equality ratio in the workplaces. Moreover, Khemka et al., (2022) in their research found that the SDGs help in the improvement of the manpower in the metropolitan MNCs through the increase in jobs in rural areas which in turn plays a significant role in enhancing the performance of the businesses in the Indian market. Furthermore, through the analysis of the findings generated from the thematic analysis it was found that the sustainable development goal number 6 is the most suitable of all the SDGs towards the expansion of the human resources performance monitoring departments as well as consulting in the Indian MNCs, especially metropolitan regions. Rahigude et al., (2022) in this regard present that the management of the 6th SDG helps HR departments develop the consulting performance monitoring unit in India towards the maintenance of sustainable business operations, specifically in the metropolitan regions. Furthermore, through the research, it was found that the challenges from which the Indian Metropolitan MNCs suffer include diversity and inclusion challenges. In this regard, Priyanka, et al., (2023) in their research state that the inability to provide adequate compensation to skilled employees also acts as a challenge for the retention of skilled employees in Indian MNCs in the Metropolitan regions. Another case example from Wipro found the organisation suffering from issues including socioeconomic inequalities and gender discrimination. In terms of strategies to mitigate the challenges, it was found that deployment of performance units can mitigate challenges related to the scarcity of skilled employees along with the usage of Employee Resource Groups for establishing a culture and WOW program for mitigating inclusivity challenges as seen in the case of Wipro.
5.2 Linking with the Objectives
Obj 1: To identify the methods of sustainable development goals for HR Consulting and performance monitoring units in the multinationals of Indian metropolitan
Based on the above research it was found that HR initiatives and consulting services insurance can readily integrate SDGs into their processes through the development of talent acquisition strategies highlighting diversity and Inclusion criteria like gender equality. This integration between HR processes and Talent Management can be considered a method of sustainable development goals for HR Consulting and performance monitoring in Indian Metropolitan MNCs. In this regard, Faemi, (2024) states that green workplaces and policies can be developed to encourage remote work and paperless operational processes. Moreover, the Performance Monitoring System for monitoring and evaluating sustainable and ethical practices can be a beneficial addition to the achievement of SDGs. Furthermore, Collaboration between multiple stakeholders for fostering sustainable practices and workforce well-being and equipment initiatives can be considered as methods to achieve sustainability with the adoption of the UN SDGs.
Obj 2: To analyze the importance of sustainable development goals in the multinationals of Indian metropolitan areas.
Through the research, it was found that one of the crucial aspects for an organisation in the Indian Metropolitan areas to manage its standards effectively is the use of integration between multinational operating systems and SDGs with the in-house HR consulting units and performance monitoring units. Furthermore, the importance of the SDGs in the multinational Businesses in the Indian Metropolitan regions can be related to the Strategic Alignment of HR practices with SDGs as the strategic alignment enables significant business improvements in terms of diversity, inclusion and exclusion. Furthermore, the SDGs in the multinational companies in the Indian Metropolitan region are also important due to their role in enhancing the performance of businesses based on sustainability matrices which further enables a holistic view ensuring accountability of sustainable practices individually and across all levels in the organisation (Ali, Kaurand Khan, 2023). Therefore, it was found that sustainable development goals are crucial aspects for multinational corporations in the Indian Metropolitan regions.
Obj 3: To evaluate the potential challenges to develop sustainable development goals for in-house HR Consulting and performance monitoring.
Through this research, several challenges that can affect the development of SDGs in the in-house HR Consulting and performance monitoring of Indian Metropolitan MNCs have been identified. Hong et al. (2022) for instance, found that in India multiple regions have prioritised environmental sustainability over social sustainability and vice-versa. This disparity in cultural and regional priorities in terms of developing a unified organisational SDG compliance framework can be detrimental. Furthermore, challenges in areas of capacity building and training, resistance to change, Measurement and Accountability, collaborative issues, global and local tensions, resource constraints and other challenges were identified. Hailu et al. (2020) for instance state, in relation to the Indian Metropolitan MNCs, that regular cross-functional meetings can help reduce the gap between global strategies and local executions of the companies. Shaw et al. (2023) in this context state that the ambitious SDG initiatives undertaken by global headquarters often cannot be implemented by local branches due to resource constraints and tensions.
Obj 4: To recommend the potential process to mitigate sustainable development goals for in-house HR Consulting and performance monitoring.
Research regarding the different challenges faced by the businesses led to the research into the strategies implemented by businesses to mitigate the issues. In this context, it was found that Waizenegger, et al., (2020) recommend the need to customise strategies based on regional priorities and workforce preferences to reduce resistance to change. Moreover, the use of KPIs to measure and control the progress towards achieving SDGs was found as another strategy. Sarwal, et al., (2021) also state that the use of transparent communication and Implementation strategies can be beneficial in reducing workforce resistance to changes brought about by implementing sustainability goals. Moreover, Public-private partnerships and mandating sustainability regulations creating synergies can also be a strategy to mitigate the challenges (Men, Yue and Liu, 2020). Other strategies identified include the use of measurement technologies and providing employee incentives for successful change.
5.3 Recommendations
Recommendation 1: Incentivising Employees
In order to truly integrate the Sustainability Strategy of the organisation and the Sustainable Management of Human Resources in the organisation, it is essential to make a proactive and adaptive analytical framework which enables the usage of non-financial mechanisms to incentivise sustainable behaviour among the employees including paid holidays, flexible working hours or certificates of recognitions (Lopez-Cabrales, and Valle-Cabrera, 2020). This demonstrates that the Indian metropolitan MNCs should focus on incentivising employees towards reducing resistance to change among the workforce, while also raising their levels of motivation towards active participation in the change through the use of incentives.
Recommendation 2: Making Sustainability strategies culturally and locally adaptive and flexible
Sudirjo, (2023) in their research demonstrate that with globalisation and increasing competitiveness between firms, it is essential for businesses to comprehensively understand the diverse background-specific and cultural demands, needs and preferences of the consumers and others, while also navigating through the distinct legislations and compliance standards set by the local countries. In this regard, the Indian Metropolitan MNCs should focus on making the global sustainability strategies of the firms adaptative and flexible for modifications according to the preferences and requirements of the local branches of the businesses. This would enable the businesses to quickly implement sustainability strategies across different local markets of the MNCs.
Recommendation 3: Green Recruitment and Screening
Jamal et al., (2021), in their research state that green recruitment and screening have a positive impact on corporate sustainability practises and require interviewers to ask more questions in relation to the environment during interviews. This process would enable the hiring of environmentally aware and ambitious employees who will strive to incorporate sustainability practises into the organisational culture thereby enhancing corporate sustainability levels. Therefore, Green Recruitment and Screening can be an optimal strategy for mitigating the challenges of employee resistance and lack of sufficient capacity and employee training.
5.4 Future Scope of the Research
The future research in continuation to the present research can focus on quantitative examining of the impact of individual SDGs and their comparative analysis towards achieving Sustainable workplace culture in business organisations. Furthermore, research can also be conducted by comparatively studying the impact of the national culture of culturally opposite countries like the UK and Japan on the effectiveness of the SDGs in allowing businesses to achieve better business performance and sustainable HR management. Moreover, research can also be conducted in relation to the ways in which the under-researched application of SDGs towards achieving business sustainability in the HR domain can lead to devastating results for the businesses due to a mismatch with the strategic direction of the business.
5.5 Summary
This section discussed and summarised the major findings of the present research connecting the findings to the main objectives of the research. This in turn showed that the research objectives were met making the research a successful endeavor. In this regard, in relation to the challenges identified specific recommendations have been suggested for application in MNCs in the Indian Metropolitan areas.
Popular Sample
Read Assignment 3's discussion paper to gain valuable insights and thorough analysis on the topic at hand. A must-read for in-depth knowledge....
Delve into cognitive development stages, key theories, and influential factors shaping human intelligence from infancy to adulthood....
Learn why transparency is crucial in digital marketing and how it can improve your brand's credibility and customer engagement....

