The Role of Operations Management in Business Growth
Task 1: Introduction
1.1 Introduction of Selected Project
Project Focus:
The paper looks at the optimization of supply chain strategies for Heathrow Airport, which is one of the busiest international airports and a global leader in connectivity.
Brief Background: Heathrow Airport and its Operations:
Heathrow Airport was opened in 1946 and has grown into one of the most important international hubs, serving more than 180 destinations in 90 countries around the world. In the busiest year of 2019, Heathrow processed 80.9 million passengers and functioned efficiently in passenger flow management, baggage handling, and logistics (Heathrow Airport, 2022).

Figure 1: Heathrow Control Tower
(Sources: Heathrow Airport, 2022)
Cargo handling is also an important part of Heathrow's operations, having processed 1.4 million tonnes of cargo in 2022 alone (Heathrow Airport, 2022). Heathrow is the best-connected airport in the world, with 89 airlines offering services to 214 destinations; hence, the number one spot in terms of being internationally connected (Heathrow Airport, 2022).
1.2 Aims and Objectives of the Report
Aim:
Assess project management tools and processes utilized in the optimization of the Heathrow supply chain.
Objectives:
- Assess the alignment of the project's outcomes with the strategic objectives of Heathrow.
- Analyze the efficiency of techniques applied to supply chain management.
- Offer some actionable recommendations on improving supply chain efficiency.
1.3 Projects and the Delivery of Organization Strategy
Definition of Project:
A project is a temporary endeavour undertaken to create a unique product, service, or result. Effective management of projects can ensure that those projects are in line with strategic objectives and support the success of an organization (Afroditi Anagnostopoulou et al., 2024). In Heathrow's case, projects such as supply chain optimization are crucial for continued global leadership and operational efficiency.
Projects' Role in Organizational Strategy:
Heathrow increases its competitive advantage, minimizes delays, and increases global connectivity by adopting sophisticated supply chain approaches (Dias and Silva, 2024). For instance, the status of Heathrow as the most internationally connected airport means that effective supply chain management is a strategic factor in maintaining its position in the market (Dulia, Esrat Farhana and Syed, 2024). Supply chain optimization also directly impacts operational issues such as delays, which improve passenger experience and have a positive economic effect (Irmak Hatıpoğlu and Ömür Tosun, 2024).
1.4 Processes of Initiating, Planning, and Managing Projects
Project Initiation: This is where the project goals are defined, stakeholders are identified, and resource availability is analyzed. Initiating supply chain projects at Heathrow will involve objectives such as a clear-cut reduction of delays in the flow of cargo among others. It works directly with over 1,200 suppliers worldwide for smooth operations.
Project Planning and Management: The most effective methods of project management at Heathrow include tools such as Gantt charts to produce schedules and critical path analysis to establish where bottlenecks may occur (Jiang et al., 2024). Predictive analytics and machine learning models allow for passenger demand and cargo forecasts. Strong handover processes ensure seamless integration of logistics improvements into business-as-usual operations.
Task 2: Critical Review of the Processes of Project Management
2.1 Topic Selection and Analysis
Topic 1: Demand Forecasting
Definition and Theoretical Underpinning: Demand forecasting is a structured approach toward ascertaining future customer demand through historical data, market trends, and statistical models (Khan, 2024). This process enables organizations to foresee the forthcoming needs and align the resources effectively. The very roots of demand forecasting are based on time series analysis, regression models, and integration of external factors such as market dynamics, economic conditions, and seasonal variation (Khedr and Sheeja, 2024). In networked systems such as airports, concepts like network effects and hub economics are important to predict and manage demand (Kumar, S., 2024). These theoretical constructs enable the airport to understand transfer passenger dynamics and interconnected flight schedules that are critical in optimizing resource allocation and operational efficiency.
Application to Heathrow's Demand-Driven Inventory Management: Heathrow Airport is among the busiest airports in the world, and it makes use of demand forecasting in the management of inventories and operation preparedness (Maheshwari and Jaggi, 2024). By studying historical data related to passenger and cargo trends, Heathrow makes sure that resources are optimally allocated. Among the key considerations are:
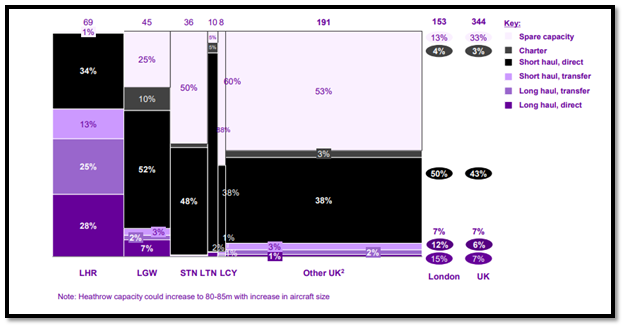
Figure 2: UK aviation passenger traffic and capacity
(Sources: Heathrow Airport Limited, 2022)
Transfer Passenger Patterns: Analysis of passengers' flow via connecting flights to identify the peak times of terminal usage (Maheshwari and Jaggi, 2024).
Peak Travel Times: Seasonal and event-based spikes in travel, such as holidays and major international events (Moghadasnian and Sadatserki, 2023).
Cargo Seasonality: to understand the changes in cargo demand, such as holiday shipping surges or fluctuations in pharmaceuticals and perishables (Moghadasnian and Sadatserki, 2023).
In 2022, Heathrow was the global hub that served the most international passengers (Heathrow Airport, 2023). The DfT has provided high-level forecasting models which are used to forecast future passenger demand to prepare plans for infrastructure and resources (Heathrow Airport, 2023).
Critical Review: Demand forecasting at Heathrow has been integral in minimizing delays and effective resource allocation; however, some aspects still require work. Of the gaps, the most prominent involves limited integration of network economics, where existing models fail to consider network effects such as flight interconnectedness and transfer passenger dynamics (Moghadasnian and Sadatserki, 2023). Additionally, while the traditional forecasting models are performing the baseline predictions, there could be a further introduction of advanced analytics and machine learning such as neural networks and ensemble methods, which would greatly increase accuracy, because the complex patterns could be determined in the runtime data (Maheshwari and Jaggi, 2024). Another related critical shortfall is the effect of sudden changes that could be geopolitical events or any other unexpected market fluctuations. Integrating real-time data and doing scenario planning could address this limitation by dynamically responding to those unforeseen conditions (Ngoudjou, G.E.T., 2024). By addressing these gaps, Heathrow will be significantly improving the accuracy and robustness of its forecasting methodologies, which are very important in putting the operation in a state of preparedness for the various challenges that lie ahead.
Topic 2: Collaboration with Suppliers
Theoretical Concepts of Supplier Management: The concept of supplier collaboration stands for developing healthy relations with the vendors for the mutual benefit of both parties (Heathrow Airport, 2023). Some key theoretical concepts include:
- Transaction Cost Economics: TCE lays emphasis on reducing costs by appropriate contractual arrangements and reducing uncertainties in transactions (Heathrow Airport, 2023).
- Relational Exchange Theory: Based on trust, openness of relations, and long-term relations that are helpful in collaborative use-innovation with mutual benefit (Sanders, N.R., 2025).
- Alignment of Strategy: Supplier incentives shall be developed in tandem with organizational goals to achieve cost efficiency, improvement in quality, and operational resilience.
Application to Heathrow's Collaboration with Global Suppliers: Heathrow operations require multi-tier networks totalling more than 1,200 supplies operating on everything from maintenance through logistics to technology service issues (Admin Here, 2024). Some key measures showing supplier performance indicate the following about suppliers.
- On-Time Delivery Rates: This refers to the timeliness of delivery of goods and services, which is very important in maintaining seamless operations.
- Lead Times: This covers the time from placing an order to the actual delivery and monitors any potential delays.
- Quality Performance: Defect rates, customer satisfaction, and return rates are measured.
- Cost Efficiency: Reduction in costs will emanate from shared process enhancement and minimizing waste (Admin Here, 2024).
Heathrow's supplier strategy involves various tools and resources, according to the scale of suppliers. Joint projects include low-carbon technology and sustainable approaches to business to support the airport's wider environment strategy (Admin Here, 2024). The benchmark against international best practices also identifies opportunities for further improvement.
Critical Review: Heathrow Airport's strategy in collaborating with its suppliers is quite effective regarding reliability and on-time delivery, though there are still some areas that need to be addressed for further improvement. Cost efficiency at the airport is below global benchmarks, indicating the need for advanced analytics to identify ineffective areas that can be streamlined to improve procurement toward better allocation of resources (Wen et al., 2024).
Moreover, while traditional methods of communicating with suppliers have been successful, the lack of digital collaboration platforms restricts transparency and agility. Integrating modern digital tools for real-time communication and performance tracking could significantly enhance supplier engagement and operational coordination (Zhou, 2024).
On the sustainability front, Heathrow's commitment to promoting eco-friendly practices is commendable, yet further investments in green supply chain technologies are essential to align supplier operations with ambitious environmental objectives (Zhou, 2024). Smoothing out these areas of improvement will enable Heathrow to reinforce stronger and resilient supplier relationships, achieve cost-effectiveness, and assure that supply chain operations remain agile, transparent, and environmentally responsible, with Heathrow's position as an aviation leader across the world cemented (Zhou, 2024).
Topic 3: Operational Logistics
Overview of Effective Logistics Processes: Operational logistics is concerned with the planning, execution, and control of flows of goods, passengers, and information. Efficiency in logistics is reached by:
- Lean Logistics: Logistics waste reduction, maximization of value in logistics operation.
- Just-In-Time Principles: Inventory cost reduction by aligning supply deliveries with demand.
- Automation and Predictive Analytics: Applying technology to automate processes and predict future needs.
- Logistics: It plays an important role at airports, as the flow of passengers and cargo must work in harmony with each other in order to contribute towards operational excellence.
Heathrow-Specific Application in Cargo Handling and Passenger Flow: Heathrow Airport handles approximately 1.4 million tonnes of cargo annually, which includes everything from books and pharmaceuticals to seafood (Heathrow Airport, 2022). On the other hand, it serves around 80 million passengers annually (Heathrow Airport, 2022). The major logistics processes include:
- Cargo Throughput: Partnerships with freight operators, routing studied for efficiency.
- Passenger Wait Times: 30-minute to 2-hour waits are common for customs processing, depending on volume and operational constraints. Peak periods of travel are often worse (Heathrow Airport, 2023).
- Baggage Handling: Advanced systems use predictive analytics to cut delays and increase handling efficiency.
Critical Review: Heathrow Airport has been engaging in a range of initiatives that work toward ensuring its logistics processes are enhanced. However, long passenger queues during peak times are still irksome; even with high-technology systems put in place, it has always worked at a disadvantage in terms of creating a customer experience. All these could have been avoided or resolved with intelligent booking and dynamic staffing policies to a greater extent. For cargo movement, all movements of vehicles at uneconomical load factors lead to higher operational costs (Afroditi Anagnostopoulou et al., 2024).
These inefficiencies could be overcome, for instance, with the implementation of real-time monitoring systems or through closer collaboration between freight shippers. Logistically, there is also great interest in alignment with the imperatives of sustainability. With more investment in low-carbon transportation and further consolidating cargo movements on rail, strong gains in sustainability metrics would be achieved with improved efficiency (Dulia, Esrat Farhana and Syed, 2024).
By prioritizing these areas for improvement, Heathrow will be able to further refine its operations by smoothing passenger flow, efficiently using cargo-carrying vehicles, and introducing sustainable logistics practices. This would not only result in cost efficiency for the company but also help to further establish Heathrow as one of the best airports in the world, maintaining its prestige related to operational excellence and sustainable growth.
Task 3: Conclusion and Recommendations
3.1 Factors of Effective Management
At Heathrow, success is founded on strategic demand forecasting, operational efficiency, and strong supplier partnerships, all working in harmony to fuel growth and the resulting economic impact. Working closely with the CAA, Heathrow has refined its forecasting models so that it correctly forecasts passenger demand to surge by 2030 (Consumers and Markets Group, 2022). Placing a strong focus on network economics and transfer passenger demand, it has been able to maintain a competitive position within the global aviation market.
The "Team Heathrow" initiative underlined the strong relationships which the airport has with more than 320 businesses, employing 76,000 people and committed to economic inclusivity (Consumers and Markets Group, 2022). In 2022, Heathrow spent £1.24 billion on 1,150 suppliers, showing that it continues to play an important part in the UK economy (Consumers and Markets Group, 2022). Heathrow supports 190,000 jobs and contributes £9.7 billion to the UK's Gross Added Value, making it an economic generator (Consumers and Markets Group, 2022).
It also refers to Heathrow's successful operational performance due to its efficient cost management policies, reviewed by organisations such as Cambridge Economic Policy Associates (CEPA), and its concentration on sustainability and productivity with the goal of decreasing operational costs while being able to meet environmental challenges.
3.2 Areas for Improvement
However, Heathrow has also been facing quite a few challenges in addition to these achievements. First, the COVID-19 pandemic reduced passenger numbers and financial losses due to the inability to work fully, which in turn led to staffing shortages at Heathrow (Ali, 2024). It particularly suffered from personnel shortages in areas like security and ground handling, which are vital for the functioning of an airport. These vacancies need to be filled to increase demand and enhance operational efficiency.
A third runway at Heathrow Airport, for instance, has provoked opposition centred on noise pollution, air quality, and climate change from environmental groups (Jovanović , 2022). These have brought about protests that have impacted operations and public perception and, therefore, have been fully addressed with careful attention to environmental sustainability.
While third-party projects are innovative in their own right, such as DHL's autonomous vehicles, efficiency in the supply chain is still lacking, particularly in cargo operations (Jovanović, 2022). A significant proportion of cargo-carrying vehicles travel to the Cargo Centre at Heathrow under capacity, which, again, simply points to an area where effective logistics could play a role in improving the outcome (Moghadasnian et al., 2023). Further expanding the use of real-time analytics for resource allocation and decision-making might promote this even more effectively.
3.3 Recommendations
Improved operational efficiency: Heathrow increases its cargo efficiency by applying AI and IoT; the airports will be able to optimize their delivery schedules, reducing the number of empty trips. Any staffing shortfalls should be addressed through targeted recruitment and training programs. Heathrow Airport also needs to invest more in sustainability by using renewable energy in conjunction with noise reduction technologies to bury concerns about its environmental impact.
The greater aviation industry should be looking to adopt AI-powered analytics for predictive maintenance, passenger flow management, and operational forecasting. Most especially, collaborative innovation, in particular with technology companies, will let the use of autonomous systems drive operational efficiency. Looking at other industries like manufacturing, the sector could use IoT for real-time monitoring, and AI-powered digital twins for scenario simulations-thus building resilience against disruption (Jovanović, 2022).
Addressing these challenges, coupled with the implementation of innovative solutions, will go a long way to help Heathrow maintain its lead within the aviation sector while continuing to grow economically.
Popular Sample
Read Assignment 3's discussion paper to gain valuable insights and thorough analysis on the topic at hand. A must-read for in-depth knowledge....
Delve into cognitive development stages, key theories, and influential factors shaping human intelligence from infancy to adulthood....
Learn why transparency is crucial in digital marketing and how it can improve your brand's credibility and customer engagement....